On November 1, 2019, CMS released the 2020 Quality Payment Program (QPP) Final Rule under the MACRA (Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act of 2015) law.
Category and General Rule Changes for 2020:
Performance Threshold / Payment Adjustment:
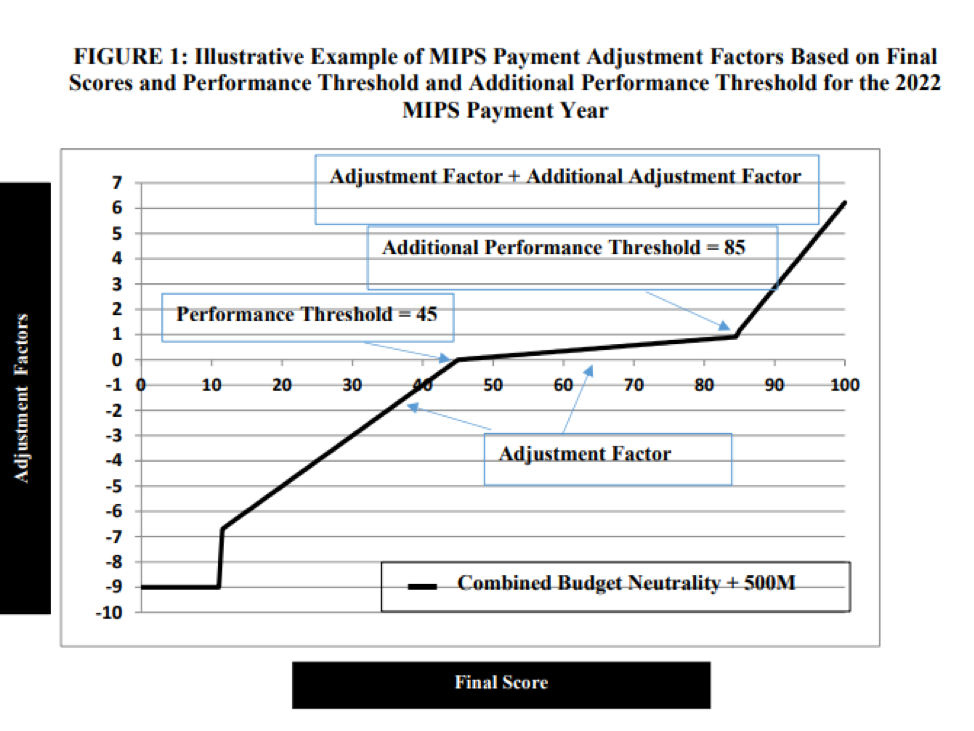
- Payment adjustment for the 2022 payment year ranges from - 9% to + (9% x scaling factor) as required by law. (The scaling factor is determined in a way so that budget neutrality is achieved).
- The average expected payment increase is estimated to be 1.4%.
- The maximum bonus is estimated by CMS to be 6.25% for clinicians that reach a MIPS score of 100 on 2020 MIPS reporting.
- The 2019 payment adjustments varied between -5% and 1.68%.
-
2017 MIPS Points 2019 MIPS Payment Adjustment 0 -4% 3 (Performance threshold) 0% 10 0.02% 20 0.05% 30 0.08% 40 0.11% 50 0.13% 60 0.16% 70 (Exceptional performance threshold) 0.29% 80 0.82% 90 1.35% 100 1.88% 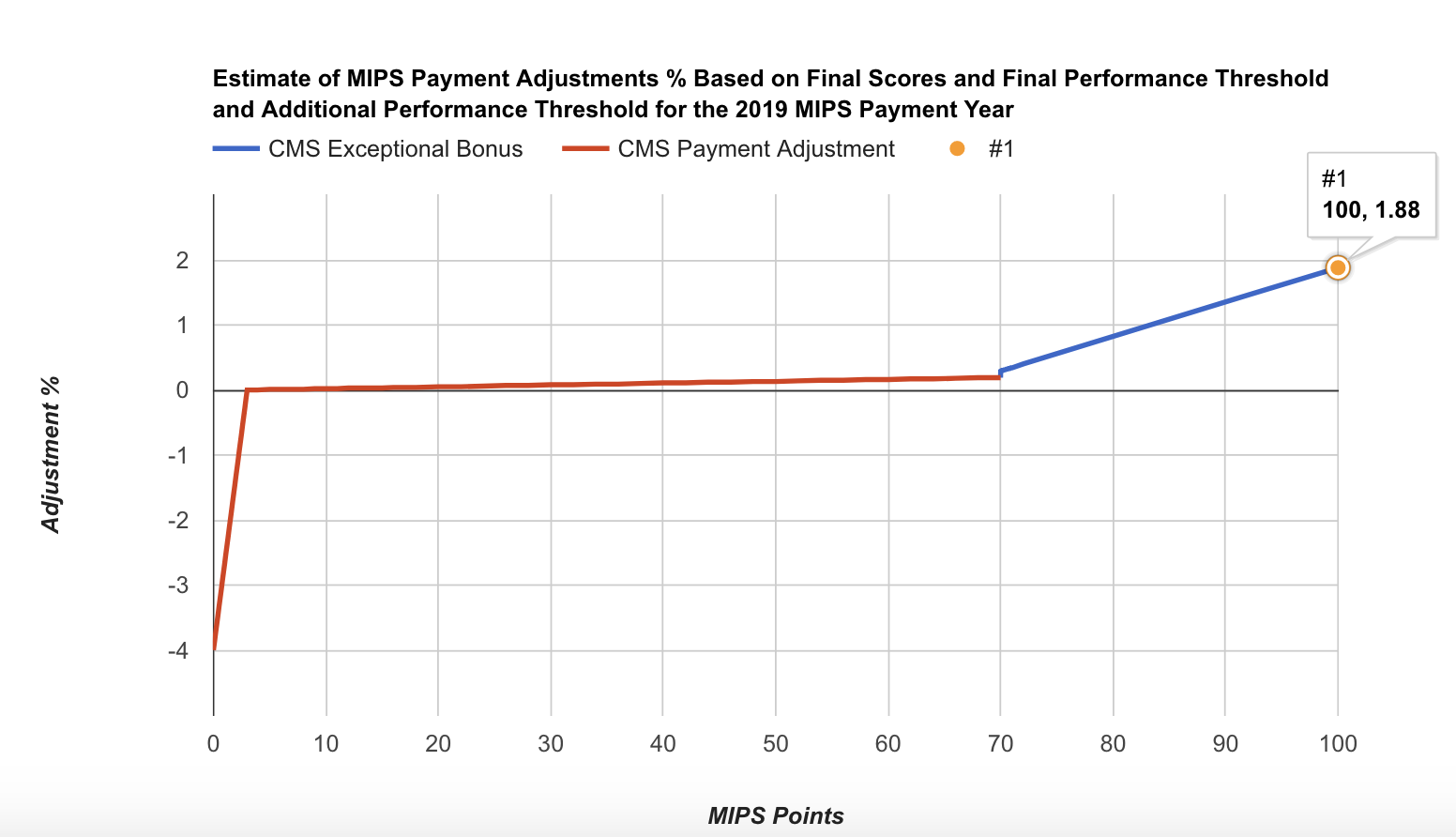
- Performance threshold increases to 45 points for 2020 MIPS (up from 30 points in 2019).
- Additional performance threshold increases to 85 points for exceptional performance for 2020 MIPS (up from 75 points in 2019).
- In the 2022 MIPS payment year, MIPS payment adjustments, which only apply to covered professional services (and does not includes Part B drugs), will be applied based on MIPS eligible clinicians’ performance on specified measures and activities within four integrated performance categories.
- CMS estimates that MIPS payment adjustments will be approximately equally distributed between negative MIPS payment adjustments ($433 million) and positive MIPS payment adjustments ($433 million) to MIPS eligible clinicians, as required by the statute to ensure budget neutrality.
- Positive MIPS payment adjustments will also include up to an additional $500 million for exceptional performance to MIPS eligible clinicians whose final score meets or exceeds the exceptional performance threshold of 85 points.
- CMS estimates that 92.5% of MIPS eligible clinicians that participate in MIPS are expected to receive positive or neutral payment adjustments.
- The final MIPS payment adjustments will be determined by the distribution of final scores across MIPS eligible clinicians and the performance threshold:
- More MIPS eligible clinicians above the performance threshold means the scaling factors would decrease because more MIPS eligible clinicians receive a positive MIPS payment adjustment factor.
- More MIPS eligible clinicians below the performance threshold means the scaling factors would increase because more MIPS eligible clinicians would receive a negative MIPS payment adjustment factor and relatively fewer MIPS eligible clinicians would receive a positive MIPS payment adjustment factor.
MIPS Eligibility:
- Eligible clinician types remain the same as 2019.
- CMS would maintain a single MIPS determination period that would be used for purposes of the low-volume threshold and to identify MIPS eligible clinicians as non-patient facing, a small practice, hospital-based, and ASC-based, as applicable:
- An initial 12-month segment beginning on October 1, 2018 to September 30, 2019; and
- A second 12-month segment beginning on October 1, 2019 to September 30, 2020.
- If a TIN or TIN/NPI did not exist in the first segment, but does exist in the second segment, these eligible clinicians could be eligible for MIPS. For example, the eligible clinician may not find their TIN or TIN/NPI in the QPP lookup tool, but may still be eligible if they exceed the low-volume threshold in the second segment.
- No Change in the Low-Volume Threshold (LVT):
- To be excluded from MIPS, clinicians or groups would need to meet one of the following three critera:
- Have ≤ $90K in Part B allowed charges for covered professional services,
- Provide care to ≤ 200 Part B enrolled beneficiaries, OR
- Provide ≤ 200 covered professional services under the Physician Fee Schedule (PFS)
- To be excluded from MIPS, clinicians or groups would need to meet one of the following three critera:
- MIPS Opt-in:
- Clinicians or groups will be able to opt-in to MIPS again in 2020 if they meet or exceed at least 1, but not all three, of the low-volume threshold criterion.
- Individual clinicians and groups could make an election to opt-in or voluntarily report MIPS via the Quality Payment Program portal by logging into their account and selecting either the option to opt-in (positive, neutral, or negative MIPS adjustment) or to remain excluded and voluntarily report (no MIPS adjustment).
- Clinicians and groups opting-in to participate in MIPS would be considered MIPS eligible clinicians, and therefore subject to the MIPS payment adjustment factor. Once the clinician or group elects to opt-in to MIPS, the decision is irrevocable and cannot be changed for the applicable performance period.
- Clinicians who do not decide to opt-in to MIPS would remain excluded and may choose to voluntarily report. Such clinicians would not receive a MIPS payment adjustment factor.
Performance Categories and Performance Period:
- Quality: 12-month calendar year performance period.
- Cost: 12-month calendar year performance period.
- Promoting Interoperability: 90 days minimum performance period.
- Improvement Activities: 90 days minimum performance period.
Quality:
- Weight to final score: 45% (same as 2019).
- Report 6 measures, including one Outcome or other High Priority measure for 12 months on at least 70% of eligible encounters to possibly earn more than 3 points on a measure. Note: Small practices (less than 16 in the practice) can earn 3 points on a measure if at least 1 eligible case is reported.
- Data completeness: completeness threshold is increased to 70% (up from 60% in 2019) of eligible cases over the entire year, regardless of payer.
- Scoring: Maintains 3-point floor for measures scored against a benchmark. Maintains 3 points for measures that don’t have a benchmark or don’t meet case minimum requirement. Measures that do not meet data completeness requirements will get 0 points instead of 1 point, except that small practices (15 or less in the TIN) will continue to get 3 points.
- Small practices would still receive a 6 point bonus added to the Quality performance score.
- Improvement Scoring for Quality: Improvement scoring continues to be based on the rate of improvement so that higher improvement will result in more points. Improvement is measured at the Quality performance category level. Up to 10 percentage points available in the Quality performance category.
- High Priority Bonus Points Remain the Same (after first required measure):
- 2 points for outcome, patient experience;
- 1 point for other high priority measures which need to meet data completeness, case minimum, and have performance greater than 0;
- Capped bonus points at 10% of the denominator of total Quality performance category;
- No high priority measure bonus points for CMS Web Interface reporters.
- There are no changes to collection types, submitter types or submission types.
- Collection type is a set of quality measures with comparable specifications and data completeness criteria, including, as applicable:
- eCQMs;
- MIPS Clinical Quality Measures (MIPS CQMs);
- QCDR measures;
- Medicare Part B claims measures;
- CMS Web Interface measures;
- CAHPS for MIPS survey;
- Administrative claims measures.
- Submitter type is the MIPS eligible clinician, group, or third party intermediary acting on behalf of a MIPS eligible clinician or group, as applicable, that submits data on measures and activities under MIPS.
- Submission type is the mechanism by which a submitter type submits data to CMS, including, as applicable:
- Direct: allows users to transmit data through a computer-to-computer interaction, such as an API.
- Log in and upload: allows users to upload and submit data in the form and manner specified by CMS with a set of authenticated credentials.
- Log in and attest: allows users to manually attest that certain measures and activities were performed in the form and manner specified by CMS with a set of authenticated credentials.
- Medicare Part B claims: only available to MIPS eligible clinicians in small practices (15 or fewer in the TIN).
- CMS Web Interface.
- Collection type is a set of quality measures with comparable specifications and data completeness criteria, including, as applicable:
Data Submission Types for MIPS Eligible Clinicians Reporting as Individuals:
|
Performance Category/Submission Combinations Accepted |
Submission Type | Submitter Type |
Collection Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality |
Direct Log in and upload Medicare Part B claims (small practices) |
Individual or Third Party Intermediary Individual |
eCQMs MIPS CQMs QCDR measures Medicare Part B claims measures (small practices) |
|
Cost |
No data submission required | Individual | - |
|
Promoting Interoperability |
Direct Log in and upload Log in and attest |
Individual or Third Party Intermediary | - |
|
Improvement Activities |
Direct Log in and upload Log in and attest |
Individual or Third Party Intermediary | - |
Data Submission Types for MIPS Eligible Clinicians Reporting as Groups:
|
Performance Category/Submission Combinations Accepted |
Submission Type | Submitter Type |
Collection Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality |
Direct Log in and upload CMS Web Interface (groups of 25 or more eligible clinicians) Medicare Part B claims (small practices) |
Group or Third Party Intermediary
|
eCQMs MIPS CQMs QCDR measures CMS Web Interface measures Medicare Part B claims measures (small practices) CMS approved survey vendor measure Administrative claims measures |
|
Cost |
No data submission required | Group | - |
|
Promoting Interoperability |
Direct Log in and upload Log in and attest |
Group or Third Party Intermediary | - |
|
Improvement Activities |
Direct Log in and upload Log in and attest |
Group or Third Party Intermediary | - |
- In 2020, individual eligible clinicians could again submit a single measure via multiple collection types (e.g. MIPS CQM, eCQM, QCDR measures and Medicare Part B claims measures) and be scored on the data submission with the greatest number of measure achievement points.
- Topped out measures: final determination of which measure benchmarks are subject to the topped out cap would not be available until the 2020 MIPS Quality Benchmarks’ file is released.
- CMS will establish flat percentage benchmarks for limited cases where CMS determines that the measure’s benchmark could potentially incentivize inappropriate treatment for some patients.
- New quality measures:
- #476 International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) or American Urological Association-Symptom Index (AUA-SI) Change 6 -12 Months After Diagnosis of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (eCQM)
- #477 Multimodal Pain Management (MIPS CQM)
- #478 Functional Status Change for Patients with Neck Impairments (MIPS CQM)
- New Endocrinology Specialty Set:
- #001: Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control
- #039: Screening for Osteoporosis for Women Aged 65-85 Years of Age\
- #117: Diabetes: Eye Exam
- #118: Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor or Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) Therapy - Diabetes or Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction (LVEF < 40%)
- #119: Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy
- #126: Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Peripheral Neuropathy – Neurological Evaluation
- #128: Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #134: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for Clinical Depression and Follow-Up Plan
- #226: Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention
- #236: Controlling High Blood Pressure
- #374: Closing the Referral Loop: Receipt of Specialist Report
- #418: Osteoporosis Management in Women Who Had a Fracture
- #438: Statin Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
- #462: Bone Density Evaluation for Patients with Prostate Cancer and Receiving Androgen Deprivation Therapy
- New Nutrition/Dietician Specialty Set:
- #001: Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control
- #128: Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #181: Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan
- #239: Weight Assessment and Counseling for Nutrition and Physical Activity for Children and Adolescents
- #431: Preventive Care and Screening: Unhealthy Alcohol Use: Screening & Brief Counseling
- New Pulmonology Specialty Set:
- #047: Care Plan
- #052: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Inhaled Bronchodilator Therapy
- #128: Preventive Care and Screening: Body Mass Index (BMI) Screening and Follow-Up Plan
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #226: Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention
- #236: Controlling High Blood Pressure
- #238: Use of High-Risk Medications in the Elderly
- #277: Sleep Apnea: Severity Assessment at Initial Diagnosis
- #279: Sleep Apnea: Assessment of Adherence to Positive Airway Pressure Therapy
- #374: Closing the Referral Loop: Receipt of Specialist Report
- #398: Optimal Asthma Control
- #431: Preventive Care and Screening: Unhealthy Alcohol Use: Screening & Brief Counseling
- #444: Medication Management for People with Asthma
- New Chiropractic Medicine Specialty Set:
- #182: Functional Outcome Assessment
- #217: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Knee Impairments
- #218: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Hip Impairments
- #219: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Lower Leg, Foot or Ankle Impairments
- #220: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Lumbar Spine Impairments
- #221: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Shoulder Impairments
- #222: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Elbow, Wrist or Hand Impairments
- #478 Functional Status Change for Patients with Neck Impairments (new measure)
- New Clinical Social Work Specialty Set:
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #134: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for Clinical Depression and Follow-Up Plan
- #181: Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan
- #226: Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention
- #281: Dementia: Cognitive Assessment
- #282 Dementia: Functional Status Assessment
- #283: Dementia: Neuropsychiatric Symptom Assessment
- #286: Dementia: Counseling Regarding Safety Concerns
- #370: Depression Remission at Twelve Months
- #382: Child and Adolescent Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Suicide Risk Assessment
- #383: Adherence to Antipsychotic Medications For Individuals with Schizophrenia
- #402: Tobacco Use and Help with Quitting Among Adolescents
- #431: Preventive Care and Screening: Unhealthy Alcohol Use: Screening & Brief Counseling
- New Audiology Specialty Set:
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #134: Preventive Care and Screening: Screening for Clinical Depression and Follow-Up Plan
- #154: Falls: Risk Assessment
- #155: Falls: Plan of Care
- #181: Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan
- #182: Functional Outcome Assessment
- #226: Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention
- #261: Referral for Otologic Evaluation for Patients with Acute or Chronic Dizziness
- #318: Falls: Screening for Future Fall Risk
- New Speech Language Pathology Specialty Set:
- #130: Documentation of Current Medications in the Medical Record
- #181: Elder Maltreatment Screen and Follow-Up Plan
- #182: Functional Outcome Assessment
- #226: Preventive Care and Screening: Tobacco Use: Screening and Cessation Intervention
- Removal of 42 Quality Measures:
- #046: Medication Reconciliation Post-Discharge
- #051: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Spirometry Evaluation
- #068: Hematology: Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS): Documentation of Iron Stores in Patients Receiving Erythropoietin Therapy
- #091: Acute Otitis Externa (AOE): Topical Therapy
- #109: Osteoarthritis (OA): Function and Pain Assessment
- #131: Pain Assessment and Follow-Up
- #160: HIV/AIDS: Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia (PCP) Prophylaxis
- #165: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Deep Sternal Wound Infection Rate
- #166: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG): Stroke
- #179: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Assessment and Classification of Disease Prognosis
- #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures
- #223: Functional Deficit: Change in Risk-Adjusted Functional Status for Patients with Neck, Cranium, Mandible, Thoracic Spine, Ribs, or Other General Orthopedic Impairments
- #255: Rh Immunoglobulin (Rhogam) for Rh-Negative Pregnant Women at Risk of Fetal Blood Exposure
- #262: Image Confirmation of Successful Excision of Image-Localized Breast Lesion
- #271: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive Care: Corticosteroid Related Iatrogenic Injury
- #325: Adult Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): Coordination of Care of Patients with Specific Comorbid Conditions
- #328: Pediatric Kidney Disease: ESRD Patients Receiving Dialysis: Hemoglobin Level < 10g/dL
- #329: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use at Initiation of Hemodialysis
- #330: Adult Kidney Disease: Catheter Use for Greater Than or Equal to 90 Days
- #343: Screening Colonoscopy Adenoma Detection Rate
- #345: Rate of Asymptomatic Patients Undergoing Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) Who Are Stroke Free or Discharged Alive
- #346: Rate of Asymptomatic Patients Undergoing Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA) Who Are Stroke Free or Discharged Alive
- #347: Rate of Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR) of Small or Moderate Non-Ruptured Infrarenal Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Who Are Discharged Alive
- #352: Total Knee Replacement: Preoperative Antibiotic Infusion with Proximal Tourniquet
- #353: Total Knee Replacement: Identification of Implanted Prosthesis in Operative Report
- #361: Optimizing Patient Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: Reporting to a Radiation Dose Index Registry
- #362: Optimizing Patient Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: Computed Tomography (CT) Images Available for Patient Follow-up and Comparison Purposes
- #371: Depression Utilization of the PHQ-9 Tool
- #372: Maternal Depression Screening
- #388: Cataract Surgery with Intra-Operative Complications (Unplanned Rupture of Posterior Capsule Requiring Unplanned Vitrectomy)
- #403: Adult Kidney Disease: Referral to Hospice
- #407: Appropriate Treatment of MSSA Bacteremia
- #411: Depression Remission at Six Months
- #417: Rate of Open Repair of Small or Moderate Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms (AAA) Where Patients Are Discharged Alive
- #428: Pelvic Organ Prolapse: Preoperative Assessment of Occult Stress Urinary Incontinence
- #442: Persistence of Beta-Blocker Treatment After a Heart Attack
- #446: Operative Mortality Stratified by the Five STS-EACTS Mortality Categories
- #449: HER2 Negative or Undocumented Breast Cancer Patients Spared Treatment with HER2-Targeted Therapies
- #454: Proportion of Patients who Died from Cancer with more than One Emergency Department Visit in the Last 30 Days of Life
- #456: Proportion Not Admitted To Hospice
- #467: Developmental Screening in the First Three Years of Life
- #474: Zoster (Shingles) Vaccination
Improvement Activities:
- Weight to final score: 15%
- No change in the number of activities that MIPS eligible clinicians have to report to reach a total of 40 points. MIPS eligible clinicians in small practices and practices in a rural areas will keep reporting on no more than 2 medium or 1 high-weighted activity to reach the highest score. Large practices attest to either 2 high weighted, 4 medium weighted or 1 high and 2 medium weighted activities for full credit in this category.
- For group reporting, the participation threshold is increased from a single clinician to 50% of the clinicians in the practice. At least 50% of the clinicians in the group must perform the same activity during any continuous 90-day period, or as specified in the activity description, within the same performance period.
- Concludes the CMS Study on Factors Associated with Reporting Quality Measures.
- Rural area is changed to mean a ZIP code designated as rural by the Federal Office of Rural Health Policy (FORHP) using the most recent FORHP Eligible ZIP Code file available.
- New Improvement Activities:
- lA BE 25 Drug Cost Transparency
- lA CC 18 Tracking of clinician's relationship to and responsibility for a patient by reporting: MACRA patient relationship codes.
- Improvement Activities Proposed for Removal:
- lA PM 1 Participation in Systematic Anticoagulation Program
- lA CC 3 Implementation of additional activity as a result ofT A for improving care coordination
- lA PSPA 14 Participation in Quality Improvement Initiatives
- lA PSPA 5 Annual Registration in the Prescription Drug Monitoring Program
- lA PSPA 24 Initiate CDC Training on Antibiotic Stewardship
- lA BMH 3 Unhealthy alcohol use
- lA BE 11 Participation in a QCDR, that promotes use of processes and tools that engage patients for adherence to treatment plan
- lA BE 2 Use of QCDR to support clinical decision making
- lA BE 9 Use of QCDR patient experience data to inform and advance improvements in beneficiary
- lA BE 10 Participation in a QCDR, that promotes implementation of patient self-action plans
- IA CC 6 Use of QCDR to promote standard practices, tools and processes in practice for improvement in care coordination
- lA AHE 4 Leveraging a QCDR for use of standard questionnaires
- lA AHE 2 Leveraging a QCDR to standardize processes for screening
- lA PM 10 Use of QCDR data for quality improvement such as comparative analysis reports across patient populations
- IA CC 4 Participation in CMS Transforming Clinical Practice Initiative
Promoting Interoperability:
- Weight to final score: 25%
- MIPS eligible clinicians must continue to use 2015 Edition certified EHR technology to report this category.
- The scoring methodology, including a smaller set of objectives, generally remains the same.
- Beginning with the 2019 performance period:
- Allows clinicians to satisfy the optional Query of Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) measure with a yes/no response instead of a numerator/denominator;
- Redistributes the points for the Support Electronic Referral Loops by Sending Health Information measure to the Provide Patients Access to Their Health Information measure if an exclusion is claimed.
- Beginning with the 2020 performance period, CMS removes the Verify Opioid Treatment Agreement measure and keeps the Query of PDMP measure as optional.
- Maintains small set of objectives:
- e-Prescribing:
- e-prescribing
- Query of Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP)
- Health Information Exchange:
- Support Electronic Referral Loops By Sending Health Information Measure
- Support Electronic Referral Loops By Receiving and Incorporating Health Information
- Provider to Patient Exchange:
- Provide Patients Electronic Access to Their Health Information
- Public Health and Clinical Data Exchange (choose 2)
- Immunization Registry Reporting,
- Electronic Case Reporting,
- Public Health Registry Reporting,
- Clinical Data Registry Reporting,
- Syndromic Surveillance Reporting)
- e-Prescribing:
- A group will be identified as hospital-based and eligible for reweighting if more than 75% of the NPIs in the group meet the definition of a hospital-based individual MIPS eligible clinician.
- CMS will reweight the Promoting Interoperability performance category to 0 and reallocate the performance category weight of 25% to the Quality performance category for the following reasons:
- Automatic reweighting:
- Hospital-based MIPS eligible clinicians;
- Non-Patient Facing clinicians;
- Ambulatory Surgical Center (ASC)— based MIPS eligible clinicians, finalized retroactive to the transition year;
- Nurse practitioners, physician assistants, clinical nurse specialist, certified registered nurse anesthetists;
- Reweighting extends to additional clinician types (physical therapists, occupational therapists, speech-language pathologists, audiologists, clinical psychologists and registered dietitians and nutrition professionals).
- Continues reweighting policy through an approved hardship application.
- Automatic reweighting:
Cost:
- Weight to final score: 15% (same as 2019)
- CMS is adding 10 new episode-based measures and revising the current measures – Medicare Spending Per Beneficiary Clinician measure and Total Per Capita Cost measure
- Acute Kidney Injury Requiring New Inpatient Dialysis
- Elective Primary Hip Arthroplasty
- Femoral or Inguinal Hernia Repair
- Hemodialysis Access Creation
- Inpatient Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Exacerbation
- Lower Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage (*only for groups)
- Lumbar Spine Fusion for Degenerative Disease, 1–3 Levels
- Lumpectomy Partial Mastectomy, Simple Mastectomy Non-Emergent Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
- Renal or Ureteral Stone Surgical Treatment
- Case minimum of 10 for procedural episodes and 20 for acute inpatient medical condition episodes.
- CMS will calculate cost measure performance; no action is required from clinicians.
Additional Details:
-
CMS estimates that between 210,000 and 270,000 clinicians will become Qualifying APM Participants (QP). As a QP, an eligible clinician is exempt from the MIPS reporting requirements and payment adjustment, and qualifies for a lump sum incentive payment based on 5 percent of their aggregate payment amounts for covered professional services for the prior year. CMS estimates that the total lump sum APM incentive payments will be approximately $535-685 million for the 2022 Quality Payment Program payment year.
-
The 2020 rule offers again Virtual Group participation, which is another way clinicians can elect to participate in MIPS.
MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) beginning in 2021
- CMS will adopt MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs), a conceptual participation framework that would apply to future proposals beginning with the 2021 performance year. The goal is to move away from siloed activities and measures and move towards an aligned set of measure options more relevant to a clinician’s scope of practice that is meaningful to patient care. The MVP framework would aim to align and connect measures and activities across the Quality, Cost, Promoting Interoperability, and Improvement Activities performance categories of MIPS for different specialties or conditions. A clinician or group would be in one MVP associated with their specialty or with a condition, reporting on the same measures and activities as other clinicians and groups in that MVP.
- In addition, the MVP framework would incorporate a foundation that leverages Promoting Interoperability measures and a set of administrative claims-based quality measures that focus on population health/public health priorities, and reduce reporting burden by limiting the number of required specialty or condition specific measures so all clinicians or groups reporting on a clinical area would be reporting the same measure set(s).
- Another key component of the MVP framework proposal is that CMS would provide enhanced data and feedback to clinicians. CMS also intends to analyze existing Medicare information so that CMS can provide clinicians and patients with more information to improve health outcomes.
- CMS created some illustrative diagrams regarding the MIPS Value Pathways: